Weather
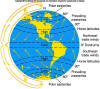
Wind belts
Clouds and fog
- Fog forms when large volumes of air come into contact with cold land or
water.
- Clouds cover about half the Earth's surface at any time.
- Clouds form when air is cooled by expansion as it rises.
- High clouds consist of ice crystals, low clouds of water droplets.
- Clouds cover about half the Earth's surface at any time.
- Clouds form through 3 chief mechanisms:
- A warm air mass moving horizontally meets a
land barrier (e.g., mountain) and rises. Coastal mountains that lie
in the paths of moisture-laden ocean winds may have permanent cloud caps
over them.
- An air mass is heated by contact with
a warm part of the earth's surface. The air mass expands, rises, and
the moisture condenses.
- A warm air mass meets a cooler air mass
and, being less dense, is forced upward over the cooler air mass. In
general, a moving cold air mass which runs into a stationary warm air
mass produces a more steeper climb of the warm air mass than would be
the case if the warm air mass ran into a cold air mass. The weather
produced by the former therefore tends to be more severe.


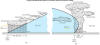
El Nino
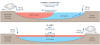
Milankovitch cycles
- Major ice ages on Earth have occurred roughly every 100,000 years, with
some smaller cycles of cold and warm at closer intervals.
- The periodicity of the Earth's glacial and interglacial cycles have been
caused primarily by changes in the Earth's orbital positions around the Sun.
Variations in the Earth's orbital positions are controlled by three dominant
cycles collectively known as the Milankovitch Cycles, named for Milutin
Milankovitch, the Serbian astronomer who is generally credited with
calculating their magnitude.
- Eccentricity is the shape of the Earth's orbit around the Sun, which
varies from more elliptic to less elliptic.
- Obliquity (or axial tilt), the angle between Earth's rotational axis
and the normal to the plane of its orbit, moves from 22.1 degrees to
24.5 degrees and back again on a 41,000-year cycle. Currently, this
angle is 23.44 degrees and is decreasing.
- Precession is the Earth's wobble on its axis as it spins. This cycle
lasts 26,000 years.
- When combined, these three cycles create variations in the amount of
solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. These times of increased or
decreased solar radiation directly influence the Earth's climate system,
thus impacting the advance and retreat of Earth's glaciers.
Return to class notes TOC.
Page last modified:


