Solution:
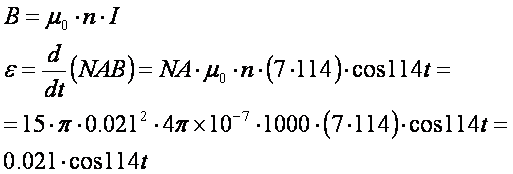
Faraday's law is basically the statement that the time derivative of the magnetic flux generates an emf. Here is an MIT lecture on motional emf.
Sample problem: A coil of 15 turns and radius 10.0 cm surrounds a long
solenoid of radius 2.10 cm and 1000 turns/meter. The current in the solenoid
changes as I = (7.00 A) sin(114 t). Find the induced emf in the 15-turn coil as
a function of time t.
Solution:
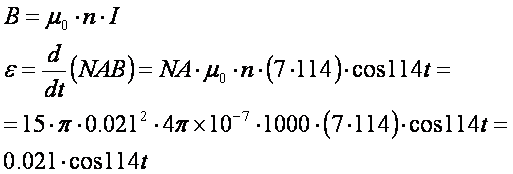
Sample problem: In a model ac generator, a 499 turn rectangular coil,
13.0 cm by 27 cm, rotates at 116 rev/min in a uniform magnetic field of 0.62 T.
What is the maximum emf induced in the coil?
Solution: In this example, the magnetic field is fixed but the loop
rotates, which produces the sinusoidally changing flux.
Return to class notes TOC.